People :Kurdish lands, rich in natural resources, have always sustained and promoted a large population. While registering modest gains since the late 19th century, but particularly in the first decade of the 20th, Kurds lost demographic ground relative to neighboring ethnic groups. This was due as much to their less developed economy and health care system as it was to direct massacres, deportations, famines, etc. The total number of Kurds actually decreased in this period, while every other major ethnic group in the area boomed. Since the middle of the 1960s this negative demographic trend has reversed, and Kurds are steadily regaining the demographic position of importance that they traditionally held, representing 15% of the over-all population of the Middle East in Asia-a phenomenon common since at least the 4th millennium BC.
Today Kurds are the fourth largest ethnic group in the Middle East, after the Arabs, Persians and Turks. Their largest concentrations are now respectively in Turkey (approx. 52% of all Kurds), Iran(25.5%), Iraq (16%), Syria (5%) and the CIS (1.5%). Barring a catastrophe, Kurds will become the third most populous ethnic group in the Middle East by the year 2000, displacing the Turks. Furthermore, if present demographic trends hold, as they are likely to, in about fifty years Kurds will also replace the Turks as the majority ethnic group in Turkey itself.
There is now one Kurdish city with a population of nearly a million (Kirminshah) , two with over half a million (Diyarbekir, Kirkuk), five between a quarter and half a million (Antep, Arbil, Hamadan, Malatya, Sulaymania), and quarter of a million people (Adiyaman, Dersim[Tunceli], Dohuk, Elazig[Kharput], Haymana, Khanaqin, Mardin Qamishli, Qochan, Sanandaj, Shahabad, Siirt and Urfa).
Religion :
Nearly three fifths of the Kurds, almost all Kurmanji-speakers, are today at least nominally Sunni Muslims of Shafiite rite. There are also some followers of mainstream Shiitem Islam among the Kurds, particularly in and around the cities of Kirmanshah, to Hamadan and Bijar in southern and eastern Kurdistan and the Khurasan. These Siite Kurds number around half a million. The overwhelming majority of Muslim Kurds are followers of one several mystic Sufi orders, most importantly the Bektashi order of the northwest Kurdistan, the Naqshbandi order in the west and north, Qadiri orders of east and central Kurdistan, and Nurbakhshi of the south.
The rest of the Kurds are followers of several indigenous Kurdish faiths of great antiquit and originality, which are variations on and permutation of an ancient religion that can be reasonably but loosely labeled as Yardanism or the "Cult of Angels." The three surviving major divisions of this religion are Yezidism (in west and west-central Kurdistan, ca 2%of all Kurds), Yarsanism or the Ahl-i Haqq (in southern Kurdistan, ca 13% of all Kurds), and Alevism or Kizil Bash(in western Kurdistan and the Khurasan, ca 20%).
Minor communities of Kurdish Jews, Christians and Baha'is are found in various croners of Kurdistan. the ancient Jewish community has progressively emigrated to Israel, while the Christian community is merging their identity with that of the Assyrians.
|

|
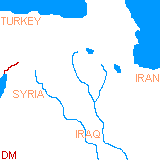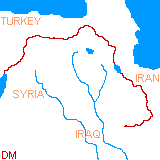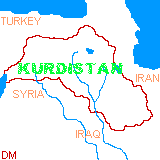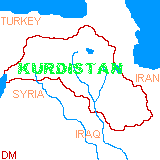
Geopolitics :Since the end of World War I, Kurdistan has been administered by five sovereign states, with the largest portions of the land being respectively in Turkey (43%) , Iran (31%), Iraq (18%), Syria (6%) and the former Soviet Union (2%).
The Iranian Kurds have lived under that state's jurisdiction since 1514 and the Battle of Chaldiran. The other three quarters of the Kurds lived in the Ottoman Empire from that date until its break-up following WWI. The French Mandate Syria received a piece, and the British incorporated central Kurdistan or the "Mosul Vilayet" and its oil fields at Kirkuk into their recently created Mandate of Iraq. Northern and western Kurdistan were to be given choice of independence by the Treaty of Sevres(August 10, 1920) which dismantled the defunct Ottoman Empire, but instead they were awarded to the newly established Republic of Turkey under the term of the Treaty of Lausanne (June 24, 1923). The Russian/Soviet Kurds had passed into their sphere in the course of the 19th century when territories were ceded by Persia/Iran.
The Kurds remained the only ethnic group in the world with indigenous representatives in three world geopolitical blocs: the Arab World (in Iraq and Syria), NATO (in Turkey), the South Asian-Central Asian bloc (in Iran and Turkmenistan), and until recently the Soviet bloc (in the Caucasus, now Armenia, Azerbaijan and Georgia). As a matter fact, until the end of the Cold War, Kurds along with the Germans were the only people in the world with their home territories used as a front line of fire by both NATO and the Warsaw Pact forces.
Language :Kurds are speakers of Kurdish, a member of the northwestern subdivision of the Iranic branch of the Indo-Europian family of languages, which is akin to Persian, and by extension to other Europian languages. It is fundamentally different from Semetic Arabic and Altaic Turkish. Modern Kurdish divides into two major groups: 1) the Kurmanji group and, 2) the Dimili-Gurani group. These are supplemented by scores of sub-dialects as well. The most popular vernacular is that of Kurmanji(or Kirmancha), spoken by about three-quarters of the Kurds today. Kurmanji divided into North Kurmanji(also called Bahdinani, with around 15 million speakers, primarily in Turkey, Syria, and the former Soviet Union) and South Kurmanji(also called Sorani, with about 6 million speakers, primarily in Iraq and Iran. To the far north of Kurdistan along Kizil Irmak and Murat rivers in Turkey, Dimili(less accurately but more commonly known as Zaza) dialect is spoken by about 4 million Kurds. There are small pockets of this language spoken in various croners of Anatolia, northern Iraq, northern Iran and the Caucasus as well.
In the far southern Kurdistan, both in Iraq and Iran, the Gurani dialect is spoken by about 3 million Kurds. Gurani along with its two major subdivisions: Laki and Awramani, merit special attention for its wealth of sacred and secular literature stretching over a millennium.In Iraq and Iran a modified version of the Perso-Arabic alphabet has been adapted to South Kurmani(Sorani). The Kurds of Turkey have recently embarked on an extensive campaign of publication in the North Kurmanji dialect of Kurmaji (Bahdinani) from their publishing houses in Europe. these employed a modified form of the Latin alphabet. The Kurds of the former Soviet Union first began writing Kurdish in the Armenian alphabet in the 1920s, followed by Latin in 1927 , then Cyrillic in 1945, and now in both Cyrilic and Latin. Gurani dialects continue to employ the Persian alphabet without any change. Dimili now uses the same modified Latin alphabet as North Kurmanji for print.
|
|
|
|